GitOps with Istio and ArgoCD
Managing Istio can be tough. Some years ago Istio 1.4.x was deployable via Helm, but was hard to manage desired state because of the massive microservice sprawl. Later on, Istio packaged the control plane services into a single istiod instance, and even provided support for Operator style deployments and an easy to use cli tool called istioctl. As of the time of this writing, Istio has deprecated Operator based deployments due to issues with webhook configurations that improperly register with the control plane.
Prerequisites
Clone the Project Repository
Clone the project:
git clone https://github.com/jonathanelbailey/homelab.catalog.git
cd homelab.catalog/istio-gitops/
Deploy Istio Base Application Resource
The following Application manifest will deploy the Istio base helm chart:
| applications/istio-base/istio-base.yaml |
|---|
| apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: istio-base
namespace: argocd
spec:
destination:
namespace: istio-system
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
project: default
source:
chart: base
repoURL: https://istio-release.storage.googleapis.com/charts
targetRevision: 1.16.5
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
retry:
backoff:
duration: 5s
factor: 2
maxDuration: 3m0s
limit: 2
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true
|
Apply it with kubectl:
kubectl apply -f applications/istio-base/istio-base.yaml
Deploy Istiod Application Resource
and here is the application manifest for deploying istiod:
| applications/istiod/istiod.yaml |
|---|
| apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: istio-base
namespace: argocd
spec:
destination:
namespace: istio-system
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
project: default
source:
chart: istiod
repoURL: https://istio-release.storage.googleapis.com/charts
targetRevision: 1.16.5
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
retry:
backoff:
duration: 5s
factor: 2
maxDuration: 3m0s
limit: 2
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true
|
Apply it with kubectl:
kubectl apply -f applications/istiod/istiod.yaml
If you check the sync status of istio-base you will notice that it is no longer synced:
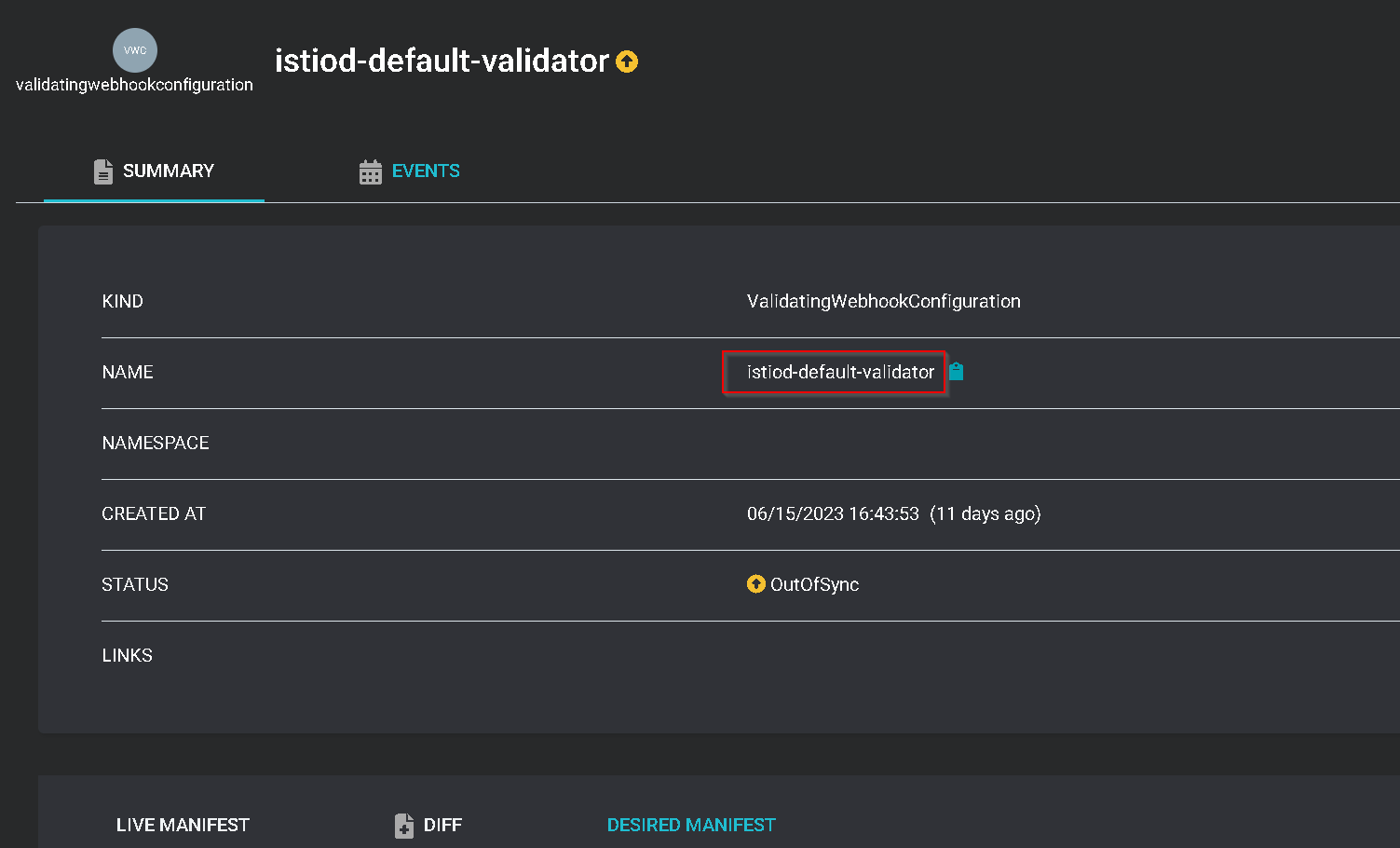
To fix this issue, we'll need to tell ArgoCD to ignore updates to istio-base by istiod:
| applications/istio-base/istio-base.yaml |
|---|
| apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: istio-base
namespace: argocd
spec:
destination:
namespace: istio-system
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
project: default
source:
chart: base
repoURL: https://istio-release.storage.googleapis.com/charts
targetRevision: 1.16.5
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
retry:
backoff:
duration: 5s
factor: 2
maxDuration: 3m0s
limit: 2
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true
# Set sync options to respect differences in managed fields
- RespectIgnoreDifferences=true
# IGNORE CHANGES MADE BY PILOT-DISCOVERY
ignoreDifferences:
- group: '*'
kind: '*'
managedFieldsManagers:
- pilot-discovery
|
And apply the updated manifest:
kubectl apply -f applications/istio-base/istio-base.yaml
When ArgoCD resyncs this change, istio-base should be fully synced and healthy.
Deploy Istio Gateway Application Resource
Next, we'll deploy an Istio Gateway using the following manifest:
| applications/istio-gateway/istio-gateway.yaml |
|---|
| apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: istio-base
namespace: argocd
spec:
destination:
# deploy to a different namespace than istiod
namespace: istio-ingress
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
project: default
source:
chart: gateway
repoURL: https://istio-release.storage.googleapis.com/charts
targetRevision: 1.16.5
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
retry:
backoff:
duration: 5s
factor: 2
maxDuration: 3m0s
limit: 2
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true
|
And apply the manifest:
kubectl apply -f applications/istio-gateway/istio-gateway.yaml
Once ArgoCD fully syncs, an istio-gateway instance will be deployed with a Service of type: LoadBalancer:
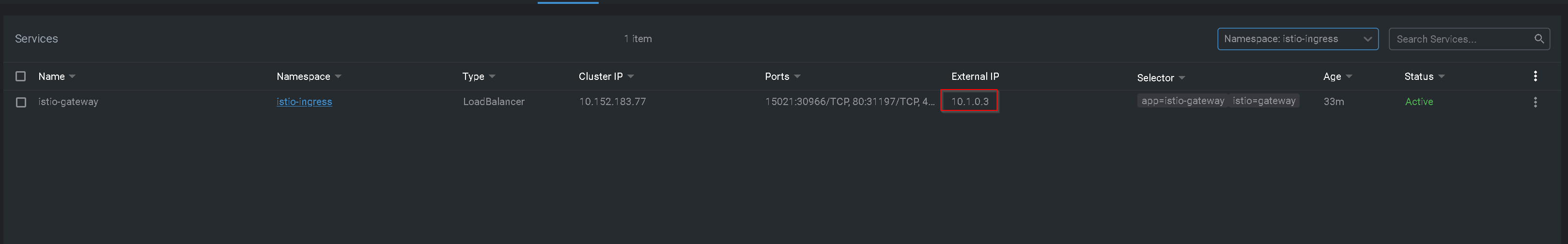
Validating the Installation
Deploy the bookinfo applications:
kubectl create ns bookinfo
kubectl label ns bookinfo istio-injection=enabled
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/release-1.18/samples/bookinfo/networking/bookinfo-gateway.yaml -n bookinfo
The gateway and virtualservice configurations are a bit different than the default:
| services/bookinfo/bookinfo-gateway.yaml |
|---|
| apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: bookinfo-gateway
spec:
selector:
istio: gateway # reflects the new gateway deployment label
servers:
- port:
number: 80
name: http
protocol: HTTP
hosts:
# Define your host, and make sure the FQDN resolves to the Istio Gateway's external IP
- "bookinfo.internal.magiccityit.com"
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: bookinfo
spec:
hosts:
# Define your host, and make sure the FQDN resolves to the Istio Gateway's external IP
- "bookinfo.internal.magiccityit.com"
gateways:
- bookinfo-gateway
http:
- match:
- uri:
exact: /productpage
- uri:
prefix: /static
- uri:
exact: /login
- uri:
exact: /logout
- uri:
prefix: /api/v1/products
route:
- destination:
host: productpage
port:
number: 9080
|
Apply the manifest:
kubectl apply -f services/bookinfo/bookinfo-gateway.yaml -n bookinfo
Check that bookinfo works by accessing http://bookinfo.internal.magiccityit.com/productpage:
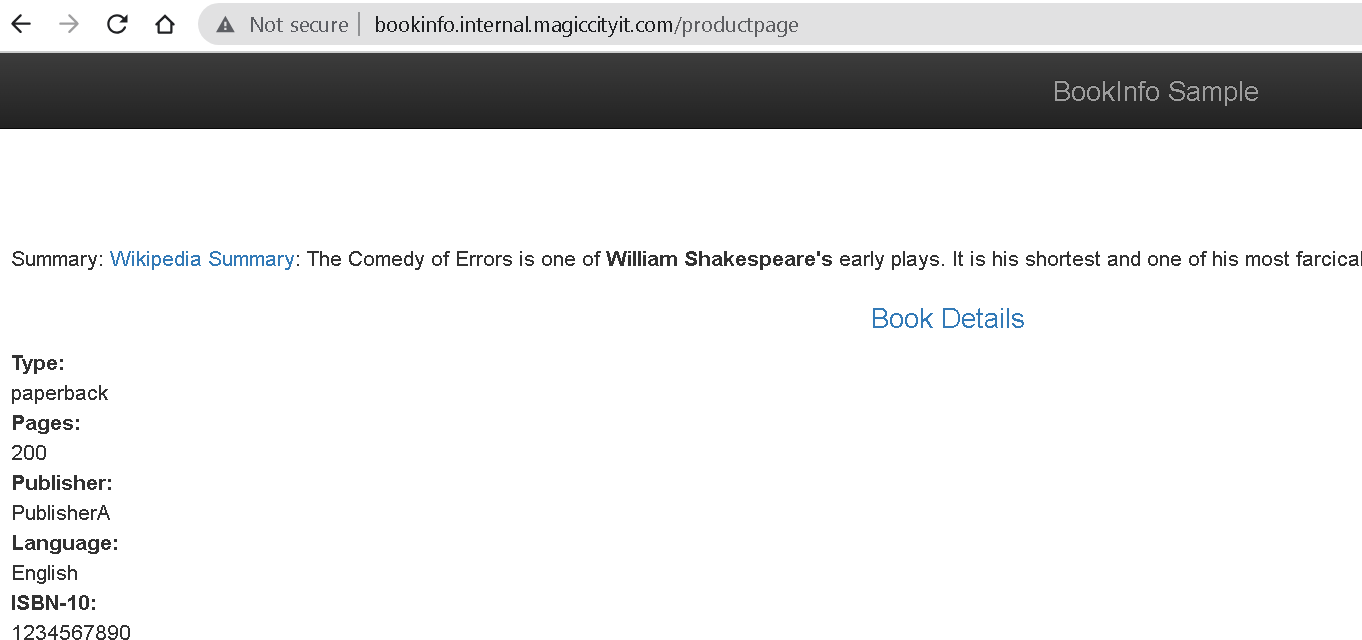
The gateway can also be updated to use TLS by configuring port 443 with an appropriate valid certificate:
| services/bookinfo/bookinfo-gateway.yaml |
|---|
| apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: bookinfo-gateway
spec:
selector:
istio: gateway # reflects the new gateway deployment label
servers:
- port:
number: 80
name: http
protocol: HTTP
hosts:
# Define your host, and make sure the FQDN resolves to the Istio Gateway's external IP
- "bookinfo.internal.magiccityit.com"
- port:
number: 443
name: https
protocol: HTTPS
hosts:
- "bookinfo.internal.magiccityit.com"
tls:
mode: SIMPLE
credentialName: internal-magiccityit-domain-tls
|
And finally apply the manifest:
kubectl apply -f services/bookinfo/bookinfo-gateway.yaml -n bookinfo
As long as the cert secret is available in the same namespace as istio-gateway, enabling TLS should be painless:
Customizing Istio
If you need to customize Istio, you can add a second source that points to the Helm values file that you would like to use. For example, let's customize istiod using the following values file:
| services/istiod/values.yaml |
|---|
| revision: "1-16-5"
revisionTags: ["stable"]
meshConfig:
enablePrometheusMerge: true
accessLogFile: /dev/stdout
accessLogFormat: |
[%START_TIME%] "%REQ(:METHOD)% %REQ(X-ENVOY-ORIGINAL-PATH?:PATH)% %PROTOCOL%" %RESPONSE_CODE% %RESPONSE_FLAGS% %RESPONSE_CODE_DETAILS% %CONNECTION_TERMINATION_DETAILS% "%UPSTREAM_TRANSPORT_FAILURE_REASON%" %BYTES_RECEIVED% %BYTES_SENT% %DURATION% %RESP(X-ENVOY-UPSTREAM-SERVICE-TIME)% "%REQ(X-FORWARDED-FOR)%" "%REQ(USER-AGENT)%" "%REQ(X-REQUEST-ID)%" "%REQ(:AUTHORITY)%" "%UPSTREAM_HOST%" %UPSTREAM_CLUSTER% %UPSTREAM_LOCAL_ADDRESS% %DOWNSTREAM_LOCAL_ADDRESS% %DOWNSTREAM_REMOTE_ADDRESS% %REQUESTED_SERVER_NAME% %ROUTE_NAME% traceID=%REQ(x-b3-traceid)%
enableTracing: true
defaultConfig:
tracing:
sampling: 100
max_path_tag_length: 99999
zipkin:
address: jaeger-tracing-collector.monitoring.svc:9411
base:
enableIstioConfigCRDs: false
validateGateway: false
|
For ArgoCD to resync istiod with this configuration, we must add a second source:
| applications/istiod/istiod.yaml |
|---|
| apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: istiod
namespace: argocd
spec:
destination:
namespace: istio-system
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
project: default
# ADD SECOND SOURCE
sources:
# Point to catalog repository
- repoURL: 'git@github.com:jonathanelbailey/homelab.catalog.git'
# Define $values variable
ref: values
targetRevision: HEAD
- chart: istiod
repoURL: https://istio-release.storage.googleapis.com/charts
targetRevision: 1.16.5
# Use istiod values file from your own repository
helm:
valueFiles:
- $values/istio-gitops/services/istiod/values.yaml
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
retry:
backoff:
duration: 5s
factor: 2
maxDuration: 3m0s
limit: 2
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true
|
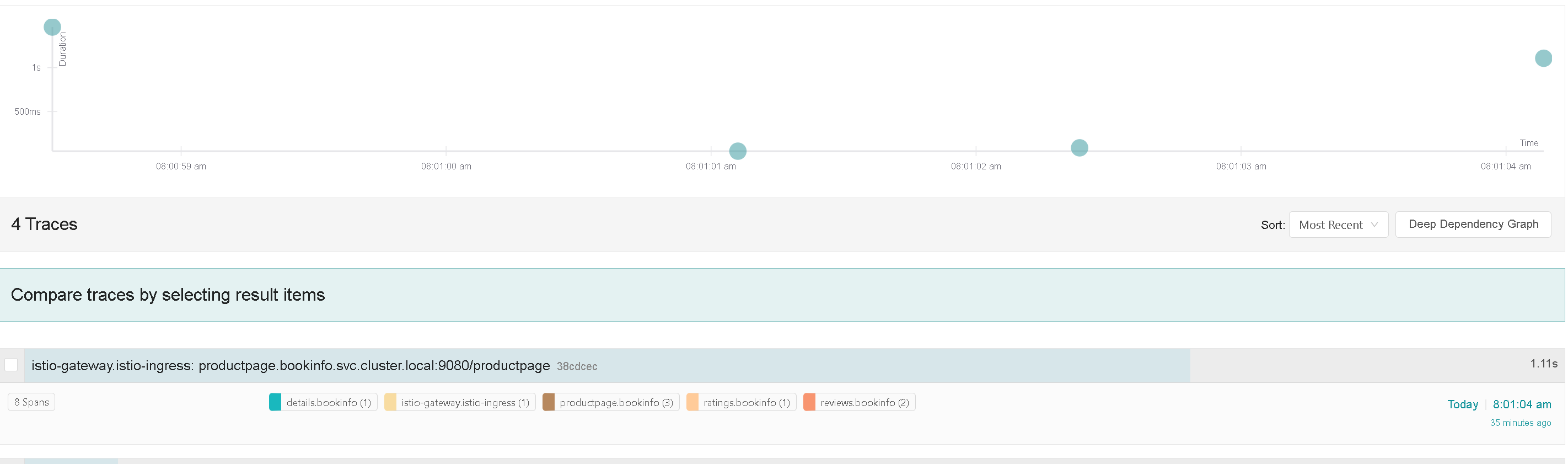
This change, among other things, enables Envoy access logs and Jaeger tracing. If you attempt to validate this change, you'll notice that there are no traces available. Run the following to ensure that everything is updated:
kubectl label ns bookinfo istio.io/rev=stable
kubectl label ns istio-ingress istio.io/rev=stable
kubectl label ns bookinfo istio-injection-
kubectl label ns istio-ingress istio-injection-
kubectl rollout restart deployment -n bookinfo
kubectl rollout restart deployment -n istio-ingress
Now you can curl https://bookinfo.internal.magiccityit.com/productpage, and the trace can finally be seen in Jaeger: